We have practical experience with many types of transcriptomic data and we offer customised data analysis and visualization to help you make the most out of your data.
What kind of analysis do we do
Methods:
- Bulk and single-cell RNA-seq analysis
- Differential expression analysis
- Time-course analysis
- Pathway analysis
- Alternative splicing
- Ribo-seq, RNA-FISH
- miRNA, tRNA fragments
Some examples:
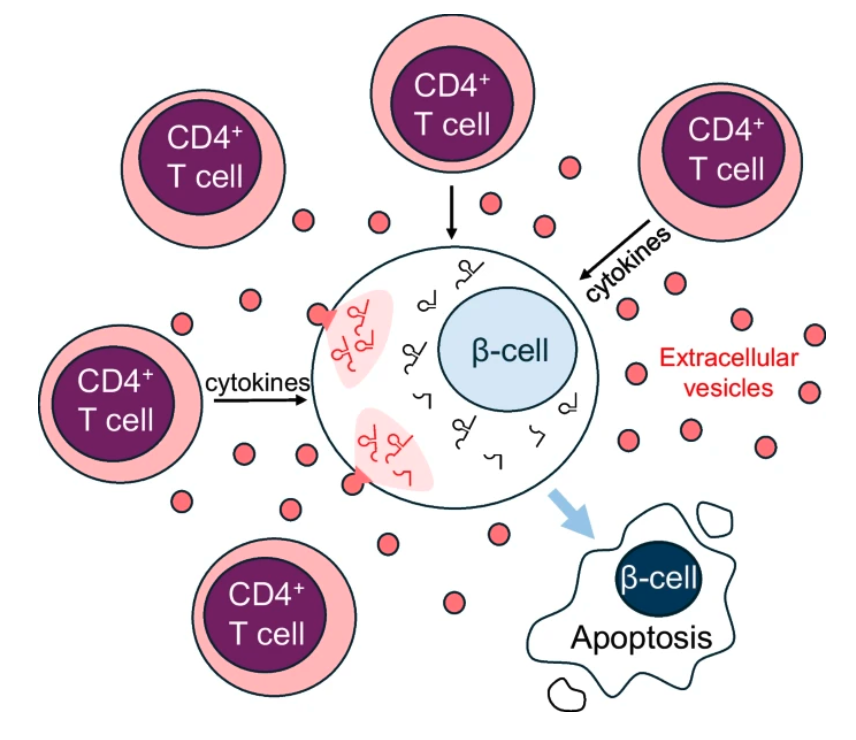
tRNA‑derived fragments in T lymphocyte–beta cell crosstalk and in type 1 diabetes pathogenesis in NOD mice
In this publication, we analysed the variation of tRNA fragments upon various conditions, to show that some tRNA fragments are transferred from T lymphocytes to beta cells during early phases of type 1 diabetes.
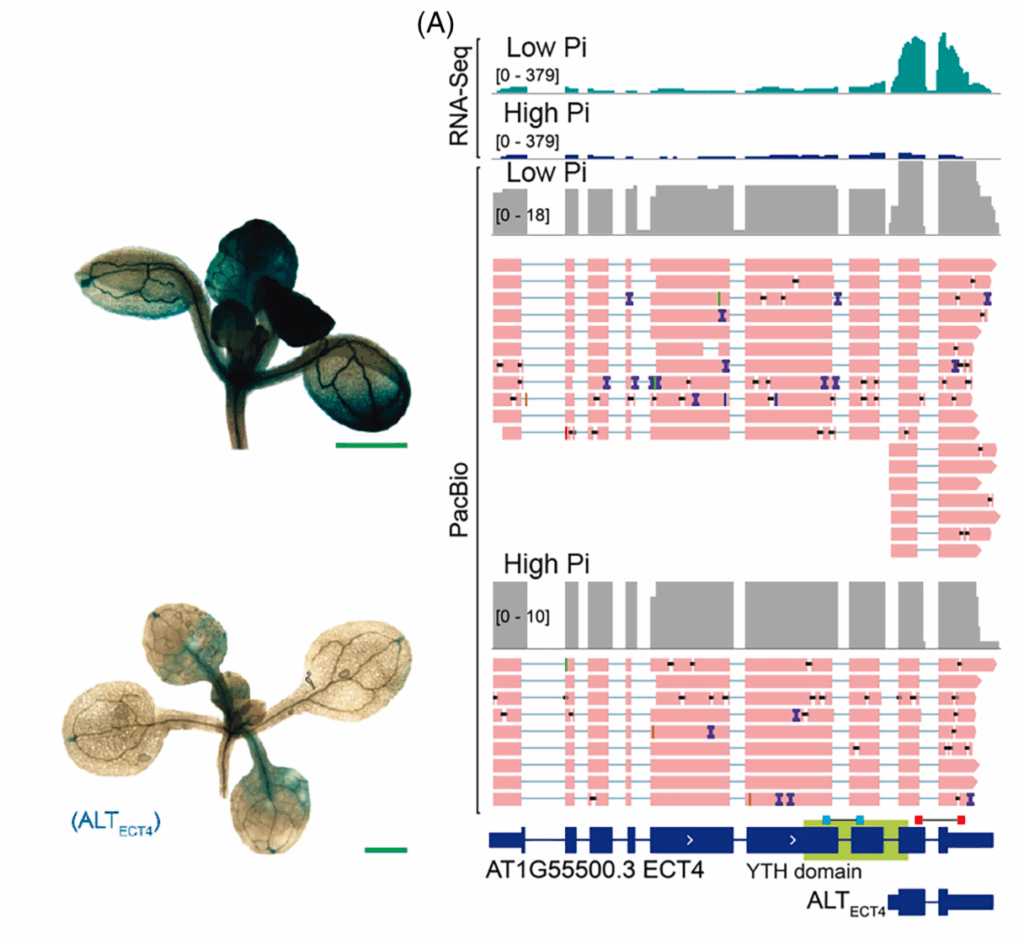
Phosphate deficiency alters transcript isoforms via alternative transcription start sites
In this publication, we looked for alternate transcripts expressed specifically under low phosphate conditions. This is the case, for example, for the EVOLUTIONARILY CONSERVED C-TERMINAL REGION 4 (ECT4) locus, which encodes an N6-methyladenosine (m6A) reader, which strongly expressed a short noncoding transcript (named ALTECT4) ~550 nt long with a TSS in the penultimate intron.
Transcriptomic Signature Differences Between SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza Virus Infected Patients
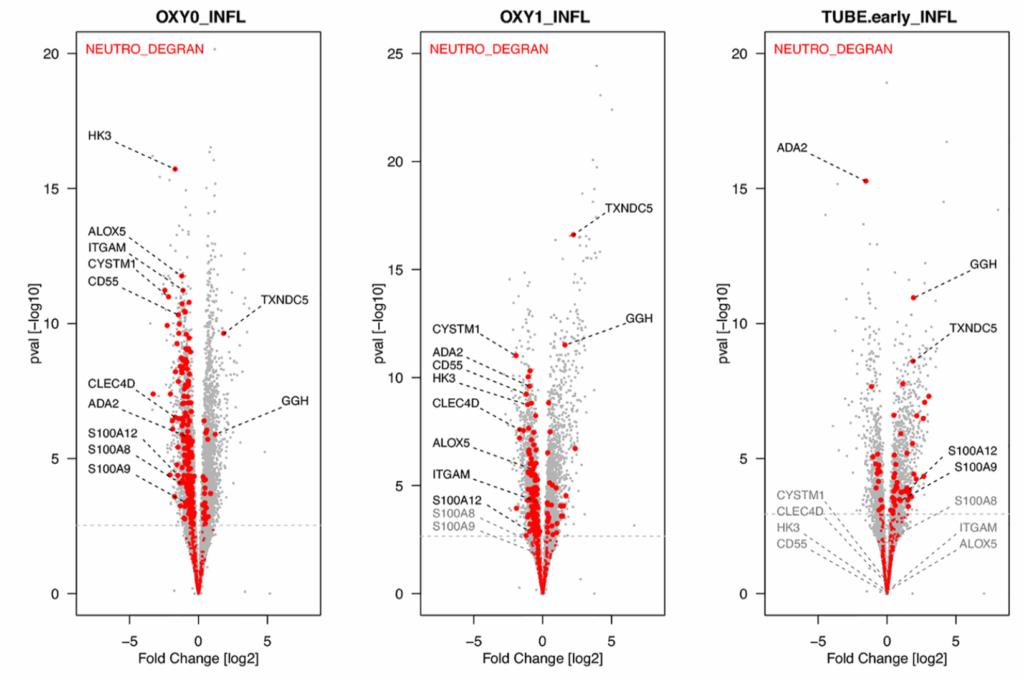
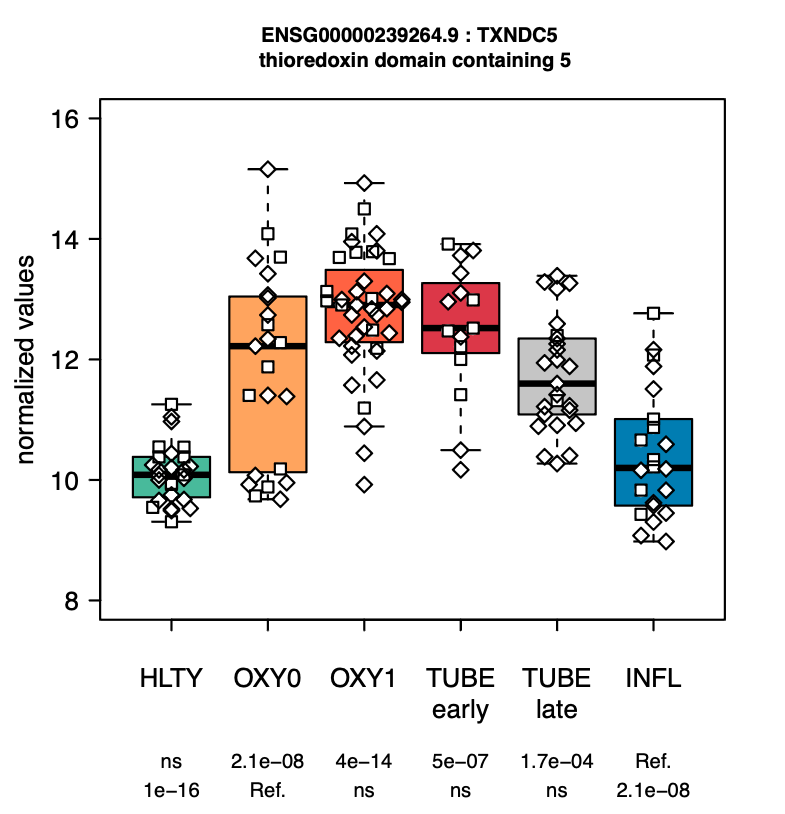
In this publication, we compared transcriptomic profiles of blood cells from 103 patients with different severity levels of COVID-19 with that of 27 healthy and 22 influenza-infected individuals. Data provided a complete overview of SARS-CoV-2-induced immune signature, including a dramatic defect in IFN responses, a reduction of toxicity-related molecules in NK cells, an increased degranulation of neutrophils, a dysregulation of T cells, a dramatic increase in B cell function and immunoglobulin production, as well as an important over-expression of genes involved in metabolism and cell cycle in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 compared to those infected with influenza viruses.
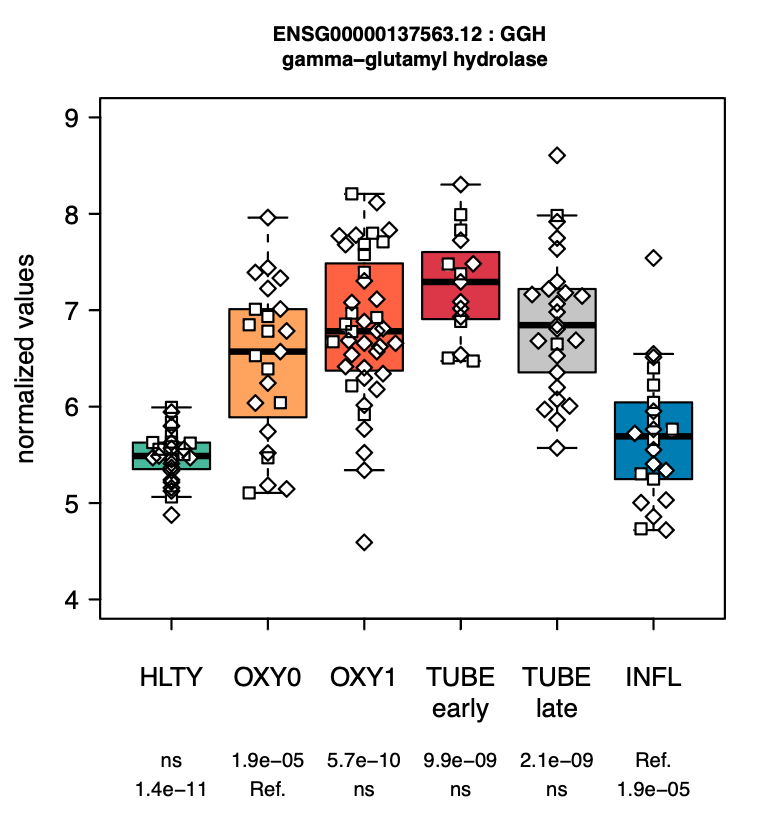
We also developed a website to facilitate the interrogation of this rich dataset, which allows to quickly identify genes such as gamma-glutamyl hydrolase (GGH) and thioredoxin domain containing 5 (TXNDC5) are dramatically upregulated in fonction of the severity of the disease, which is not the case for a severe influenza infection.